Table of contents
Journey back to 1895 when Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays, revolutionizing medicine. Explore the mechanics, medical marvels, and the beauty of crystallography with this informative piece.
The Radiant World of X-Rays: A Discovery That Changed Medicine
In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen stumbled upon a revolutionary breakthrough—the discovery of X-rays. Initially named for the unknown, these electromagnetic rays, also known as Roentgen rays, became a game-changer in medicine.
The Discovery
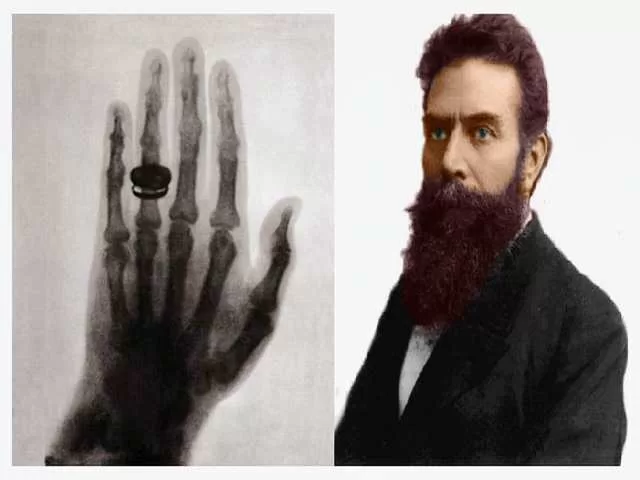
On November 8, 1895, Roentgen made history, exposing the invisible power of X-rays. Despite objections to calling them Roentgen rays, their medical potential became evident when Roentgen captured the first X-ray image—the hand of his wife. This groundbreaking moment sparked a wave of applications in healthcare.
Medical Marvel
Published in December 1895, Roentgen’s scientific paper paved the way for X-rays to be utilized in medicine. Within months, they were employed to examine broken bones and gunshot wounds. American inventor Thomas Edison contributed with the invention of a widely used fluoroscope for X-rays, although he abandoned further research due to safety concerns.
Mechanics Behind X-Ray Machines
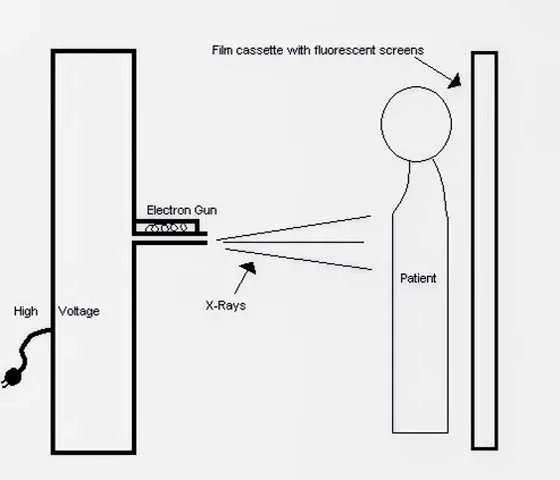
A simplified X-ray machine exposes fluorescent screens to X-rays, allowing them to pass through skin and muscle but blocking at bone or metal. The resulting image provides vital insights into internal structures, aiding in medical diagnostics.
Crystallography and Beyond
X-rays aren’t limited to medicine; they play a crucial role in crystallography. Researchers use X-rays to unravel the atomic arrangements in solids, offering stunning images that showcase the beauty of scientific exploration.
The Credit Dilemma
Roentgen is credited with the discovery, yet he wasn’t the first to notice such radiation. His systematic study and naming distinguished him. Though others had observed similar effects, Roentgen’s groundbreaking work earned him a Nobel Prize, marking a pivotal moment in the history of science.
FAQ’s About X-rays
What are X-rays and how do they work?
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate solid objects. In medical imaging, X-rays are commonly used to create detailed images of the inside of the body. They work by passing a controlled amount of radiation through the body, and different tissues absorb varying amounts of the radiation, creating a contrast that is captured on a detector.
Are X-rays safe, and should I be concerned about radiation exposure?
While X-rays are generally considered safe when used in controlled medical settings, it’s essential to minimize unnecessary exposure to radiation. The amount of radiation used in diagnostic X-rays is typically low, and the benefits of obtaining crucial medical information often outweigh the potential risks. Pregnant women and individuals with specific health conditions should inform their healthcare providers to ensure appropriate precautions are taken.
How are X-rays used in medical diagnostics?
X-rays are widely used to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. They are commonly employed to visualize bones and detect fractures, assess joint conditions, identify infections, and examine the chest for respiratory and cardiac conditions. Additionally, X-rays play a crucial role in dental imaging, mammography, and certain gastrointestinal studies.
What precautions are taken during X-ray procedures?
Radiologic technologists follow strict safety protocols to minimize radiation exposure. Patients are provided with lead aprons or shields to protect unaffected parts of their body. The use of collimators and filters helps focus the X-ray beam precisely, reducing unnecessary exposure. Pregnant women and children are particularly sensitive populations, and their exposure is carefully managed to minimize any potential risks.
How do X-rays differ from other imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs?
X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs are all imaging techniques but differ in their principles and applications. X-rays are excellent for imaging dense structures like bones, while CT scans provide more detailed cross-sectional images of soft tissues and organs. MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues and are particularly useful for neurological and musculoskeletal imaging. The choice of imaging modality depends on the specific diagnostic needs of the patient.